Guide to your first algo-trading project
Dec 23, 2024
4 min read

Xeno
seniorsde , oceanOneSecurities

These is a guide on how to start your journey on algorithmic trading, every wondered how you can execute trades into the markets in huge quantities in a matter of milliseconds? Well this is all possible due to algorithmic trading.
Traders often create multiple strategies and use those strategies to execute huge amount of trades through their engineered algorithmic model, As the name suggests algorithmic it's an adjective derived from the word "algorithm" which we know is a set of instructions or rules designed by the operator to operate functions based on the given sequence of instructions.
To get started with algo-trading we must know some handful of skills before that such as:
Mathematics
Programming
Networking
Financial Knowledge
Critical Thinking & Problem-Solving
Risk Management
It is necessary that the trader knows about these skills, as it becomes essential to the process of algo-trading.
Some tools we will be using in our tutorial are:
Visual Studio Code (Any IDE/Code editor will work like sublime, pycharm and etc.)
Python Programming Language (This is based on preference if you have experience in any other language you can proceed with that.)
Postman (This is to mock-test our websocket, you can use anything.)
.NET 4.5.2 (This is a required piece and must be this exact binary.)
Sterling DLL (This is the Sterling OEMs DLL we will be using to reach the OEMs using it's c# library.)
So we will be following a engineered model and implement according to it. I'm using eraser.io to model the structure you can use anything. This model is very basic and is not recommended to be used for PRODUCTION purposes only for learning and educational purposes. The guide only targets beginners who are looking into algo-trading
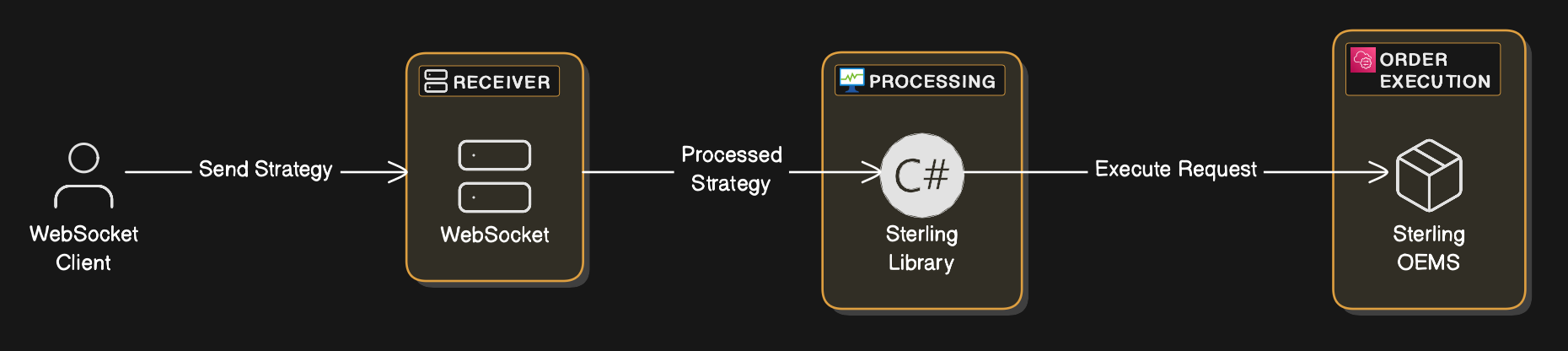
So below the process of implementation has been broken down into multiple steps.
So before we begin our websocket implementation, let's discuss what a websocket is exactly. So a websocket is like a two-way communication street for data. It's how our WebSocket Client (Your trading strategy) talks to our WebSocket Server (The python program that processes strategy), So let's set it up.
Step 1: Installing required dependencies
Start off with installing some packages, let's follow the good practice of programming.
Create a file called "requirements.txt"
1pythonnet==3.0.1
2websocket-client==1.8.0
3asyncio==3.4.3Now install these by running "pip install -r requirements.txt" in your terminal.
Step 2: Implement the websocket server
Start off by creating a "server.py" file and then import the dependencies you just installed.
1import websocket
2
3def on_message(ws, message):
4 print(f"Received: {message}")
5
6def on_open(ws):
7 print("Connection opened")
8 ws.send("Hello, Server!") # Initial message to the server
9
10def on_error(ws, error):
11 print(f"Error: {error}")
12
13def on_close(ws, close_status_code, close_msg):
14 print("Connection closed")
15
16if __name__ == "__main__":
17 ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
18 "ws://localhost:8080", # Replace with your server URL
19 on_message=on_message,
20 on_error=on_error,
21 on_close=on_close,
22 )
23 ws.on_open = on_open
24 ws.run_forever()In the code above, we have created 4 functions that represent the websocket events
on_open (emitted whenever a websocket connection is opened to the server)
on_close (emitted whenever a socket connection is closed)
on_message (when data is sent to the server)
on_error (when a exception hits the server)
Then we create a variable "ws" and set it's value to the Application instance and assign the on_open event and make sure the socket is running in a lifecycle process meaning it doesn't stop heartbeating.
Step 3: Create a websocket client
Create a file called "client.py" and paste the below piece of code.
1import websocket
2import json
3import threading
4import time
5
6def on_message(ws, message):
7 print(f"Server Response: {message}")
8
9def on_error(ws, error):
10 print(f"Error: {error}")
11
12def on_close(ws, close_status_code, close_msg):
13 print("Connection closed")
14
15def send_signals(ws):
16 try:
17 while True:
18 trading_signal = {
19 "action": "BUY",
20 "symbol": "AAPL",
21 "price": 150.00,
22 "quantity": 10
23 }
24 ws.send(json.dumps(trading_signal))
25 print(f"Signal sent: {trading_signal}")
26 time.sleep(5)
27 except KeyboardInterrupt:
28 print("Stopped sending signals")
29
30def on_open(ws):
31 print("Connection opened")
32 threading.Thread(target=send_signals, args=(ws,)).start()
33
34if __name__ == "__main__":
35 websocket_url = "ws://localhost:8080" # replace with the server url.
36 ws = websocket.WebSocketApp(
37 websocket_url,
38 on_message=on_message,
39 on_error=on_error,
40 on_close=on_close
41 )
42 ws.on_open = on_open
43 ws.run_forever()In the above code we added the client implementation for our server, and we are also sending a dummy signal for a "BUY" order on the symbol "AAPL" with quantity 10 and the limit price is set to 150$. This is a dummy signal.
So we are now prepared to test our websocket connection. run the server and the client and test the connection and you will see the connection working perfectly and smoothly.
In our next blog we will continue this setup and begin the implementation of the Sterling OEMs library into our codebase.

Still have questions?
Couldn't find the answer you're looking for? Feel free to reach out to us for assistance